数理解析に基づくMAPKシグナルと生命機能制御機構の解明
 領域代表者・研究代表者
領域代表者・研究代表者
武川睦寛
東京大学医科学研究所 分子シグナル制御分野
http://www.ims.u-tokyo.ac.jp/dcsmm/DCSMM/Top.html
研究概要
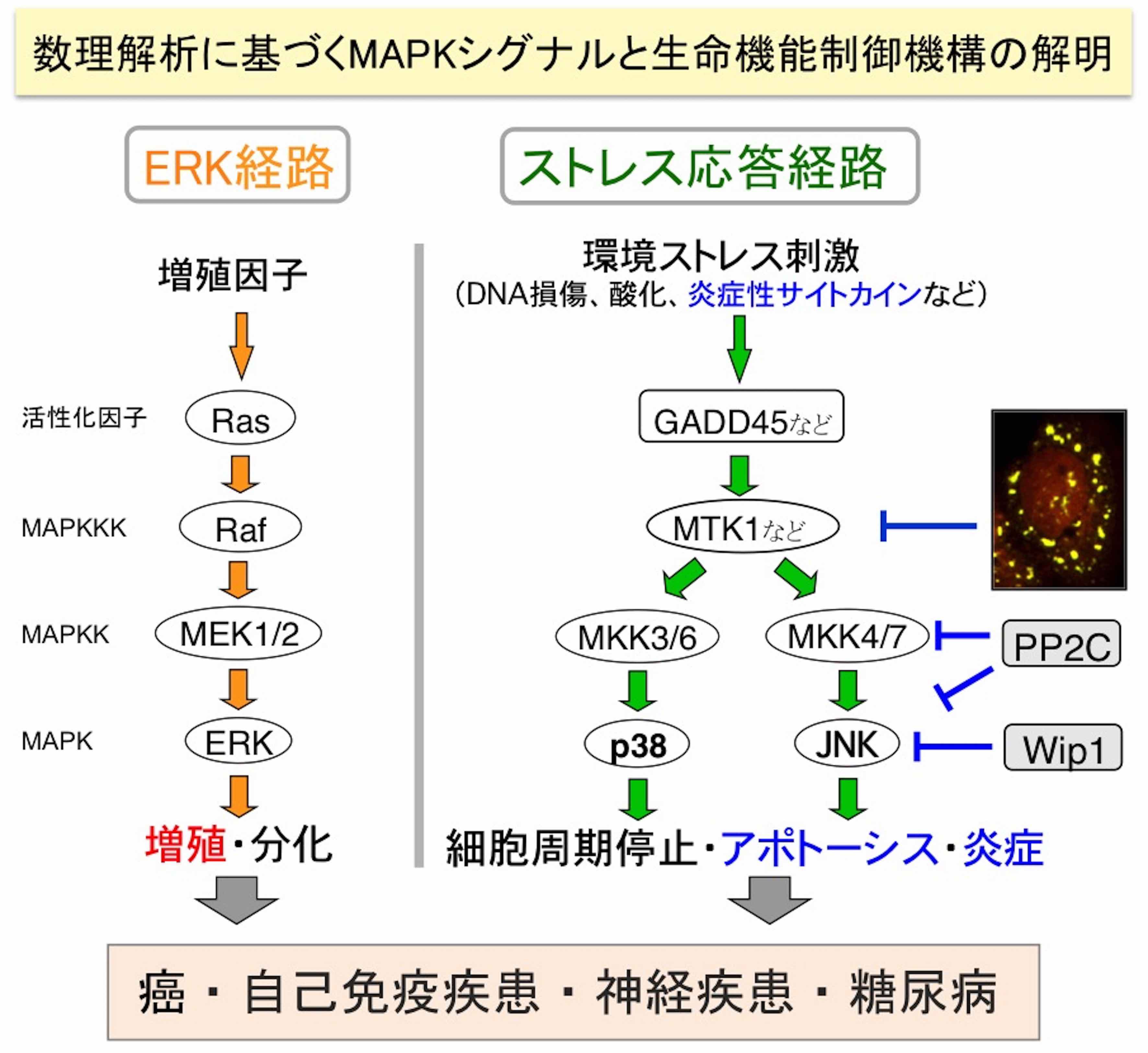
ヒト細胞内には、主に増殖因子によって活性化され、細胞増殖や生存に作用するERK経路と、様々な環境ストレス刺激に応答して活性化され、細胞死(アポトーシス)や炎症を惹起するストレス応答MAPキナーゼ(p38及びJNK)経路という、複数のMAPキナーゼ・カスケードが存在する。細胞運命(生か死か)を決定して生体の恒常性維持を担うこれらMAPK経路の制御異常が、癌、自己免疫疾患、神経変性疾患、2型糖尿病などの発症に深く関与することが明らかにされている。しかしながら、MAPK経路の活性調節機構や疾患における制御異常の詳細には、未だ不明な点が数多く残されており、その解明は疾患克服の観点からも重要である。
私達はこれまでに、MAPK情報伝達システムによる生命機能制御機構の全容解明を目指して、MAPKシグナル関連分子(活性制御分子、基質、標的遺伝子など)の網羅的解析を実施し、以下の予備データを得ている。1)MAPKによってリン酸化される基質分子を網羅的に同定する新たな手法を開発して、ヒトcDNAライブラリーのスクリーニングを行い、複数の新規基質分子を同定することに成功した。2)MAPK経路による細胞運命決定機構およびその破綻がもたらす疾患発症機構の解明を目指して、ゲノムワイドでMAPKシグナル標的遺伝子の網羅的探索を行い、多数の遺伝子を同定した。3)p38/JNK経路の活性制御に関わる細胞質内構造体、「ストレス顆粒」を構成する未知分子の網羅的な探索を行い、様々なシグナル伝達分子を同定した。
これらの知見を基に本研究では、MAPKシグナル関連分子の生理機能と疾患における制御異常を分子レベル、個体レベルで包括的に解明する。また、得られた知見を統合して、MAPK情報伝達ネットワークの数理解析を実施し、その時空間制御と生物学的アウトプット(増殖、死、免疫応答制御など)の調節機構を明らかにする。本研究を通して、MAPKシグナルによる生命機能制御の作動原理および疾患発症機構を解明すると共に、理論と実験を融合した研究の推進により、生体応答を高精度に予測し、疾患治療の鍵となる重要分子を抽出する新たな基盤技術の確立を目指す。
参考文献
- Arimoto-Matsuzaki K, Saito H and Takekawa M. TIA1 oxidation inhibits stress granule assembly and sensitizes cells to stress-induced apoptosis. Nature Commun. 7: 10252 doi:10.1038/ncomms10252 (2016)
- Ichikawa K, Kubota Y, Nakamura T, Weng JS, Tomida T, Saito H and Takekawa M. MCRIP1, an ERK substrate, mediates ERK-induced gene silencing during epithelial-mesenchymal transition by regulating the co-repressor CtBP. Molecular Cell 58: 35-46 (2015)
- Tomida T, Takekawa M and Saito H. Oscillation of p38 activity controls efficient pro-inflammatory gene expression. Nature Commun. 6: 8350 doi:10.1038/ncomms9350 (2015)
- Ohshima D, Arimoto-Matsuzaki K, Tomida T, Takekawa M and Ichikawa K. Spatio-temporal dynamics and mechanisms of stress-granule assembly. PLoS Comput. Biol. 11: e1004326 doi:10.1371/journal.pcbi.1004326 (2015)
- Nakamura T, Saito H and Takekawa M. SAPK pathways and p53 cooperatively regulate PLK4 activity and centrosome integrity under stress. Nature Commun. 4:1775 doi: 10.1038/ncomms2752 (2013)
- Tomida T, Osa S, Takekawa M, Iino Y and Saito H. The temporal pattern of stimulation determines the extent and duration of MAPK activation in a caenorhabditis elegans sensory neuron. Science Signaling 5, ra76 (2012)
- Kubota Y, O’Grady P, Saito H and Takekawa M. Oncogenic Ras abrogates MEK SUMOylation that suppresses the ERK pathway and cell transformation. Nature Cell Biol. 13, 282-291 (2011)
- Tomida T, Takekawa M, O’Grady P and Saito H. Stimulus-specific distinctions in spatial and temporal dynamics of stress-activated protein kinase kinase kinases revealed by FRET biosensor. Mol. Cell. Biol. 29, 6117-6127 (2009)
- Arimoto K, Fukuda H, Imajoh-Ohmi S, Saito H, and Takekawa M. Formation of stress granules inhibits apoptosis by suppressing stress-responsive MAPK pathways. Nature Cell Biol.10: 1324-1332 (2008)
- Takekawa, M., Tatebayashi, K., and Saito, H. Conserved docking site is essential for activation of mammalian MAP kinase kinases by specific MAP kinase kinase kinases. Molecular Cell 18, 295-306 (2005)
- Takekawa, M. and Saito, H. A family of stress-inducible GADD45-like proteins mediate activation of the stress-responsive MTK1/MEKK4 MAPKKK. Cell 95, 521-530, (1998)








